There are various forms of protected areas, which differ in the type and scope of protection: National parks, biosphere reserves, nature reserves, landscape conservation areas, nature parks, natural monuments and protected landscape features.
The following protected area categories can be found in the city of Wolfsburg: Biosphere reserves, nature reserves and landscape conservation areas, natural monuments and protected landscape features.

-
Natura 2000

In order to counteract the continuing decline of wild species and natural habitats in the EU and to preserve biodiversity, the Birds Directive was adopted in 1979 and the Habitats Directive in 1992. The core provision of both directives is the designation of protected areas to create an EU-wide "Natura 2000" network of protected areas for certain endangered species and habitat types of Community interest.
With around 27,000 protected areas covering 18.6 percent of the EU's land area, Natura 2000 is the largest transboundary, coordinated network of protected areas in the world. It makes an important contribution to the protection of biodiversity in the EU.
The Habitats Directive lists more than 200 habitat types (Annex I, 92 of which occur in Germany) and around 1,000 species and subspecies (Annex II, 138 of which occur in Germany) of Community interest for the European Union, for which a system of networked protected areas must be established. According to the Birds Directive, special protection areas must be designated for 193 species (Annex I, 110 of which occur in Germany) as well as for other regularly occurring migratory bird species.
In Germany, there are a total of over 4,500 FFH areas and 742 bird sanctuaries, some of which overlap. In total, 15.5 percent of Germany's land area and around 45 percent of its marine area are covered by Natura 2000 protected areas.
A uniform protection regime applies to the entire European Natura 2000 network of protected areas. In addition to the regulations for the necessary conservation measures and the prohibition of deterioration of this valuable natural heritage, this also includes the so-called FFH impact assessment. This instrument serves to protect Natura 2000 sites from plans or projects that could significantly affect a site in this network. For example, construction projects or certain management practices in or around Natura 2000 sites must be subject to such an assessment if they could be accompanied by an intensification of use or other negative impacts on the respective site. In order to prevent damage to Natura 2000 sites, plans and projects that have a significant negative impact are generally not permitted. However, under certain conditions and in conjunction with sufficient compensation, such plans or projects can be approved in an exceptional procedure.Parts of the following three FFH and three bird protection areas can be found in the city of Wolfsburg:
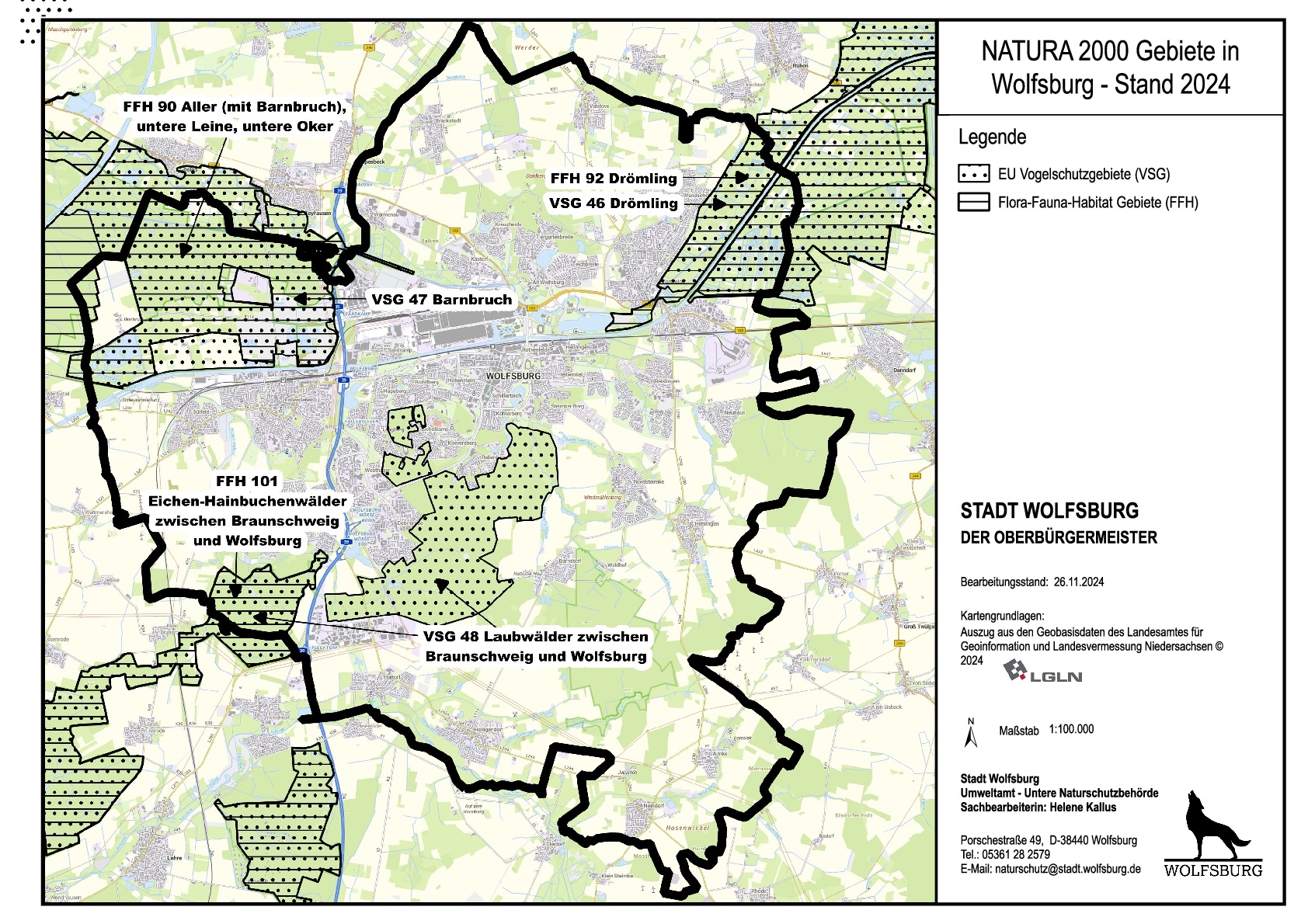 Map of the NATURA 2000 areas in WolfsburgGraphic: Lower Nature Conservation Authority Wolfsburg
Map of the NATURA 2000 areas in WolfsburgGraphic: Lower Nature Conservation Authority Wolfsburg -
Nature reserves
In accordance with Section 23 of the Federal Nature Conservation Act (BNatSchG), nature conservation areas are bindingly designated areas in which special protection of nature and landscape in their entirety or in individual parts is required
- for the conservation, development or restoration of habitats, biotopes or communities of certain wild animal and plant species
- for scientific, natural history or regional history reasons or
- because of their rarity, special character or outstanding beauty.
All actions that could lead to the destruction, damage or alteration of the nature reserve or its components or to lasting disturbance are prohibited.
The following eight nature reserves are located in the city of Wolfsburg:
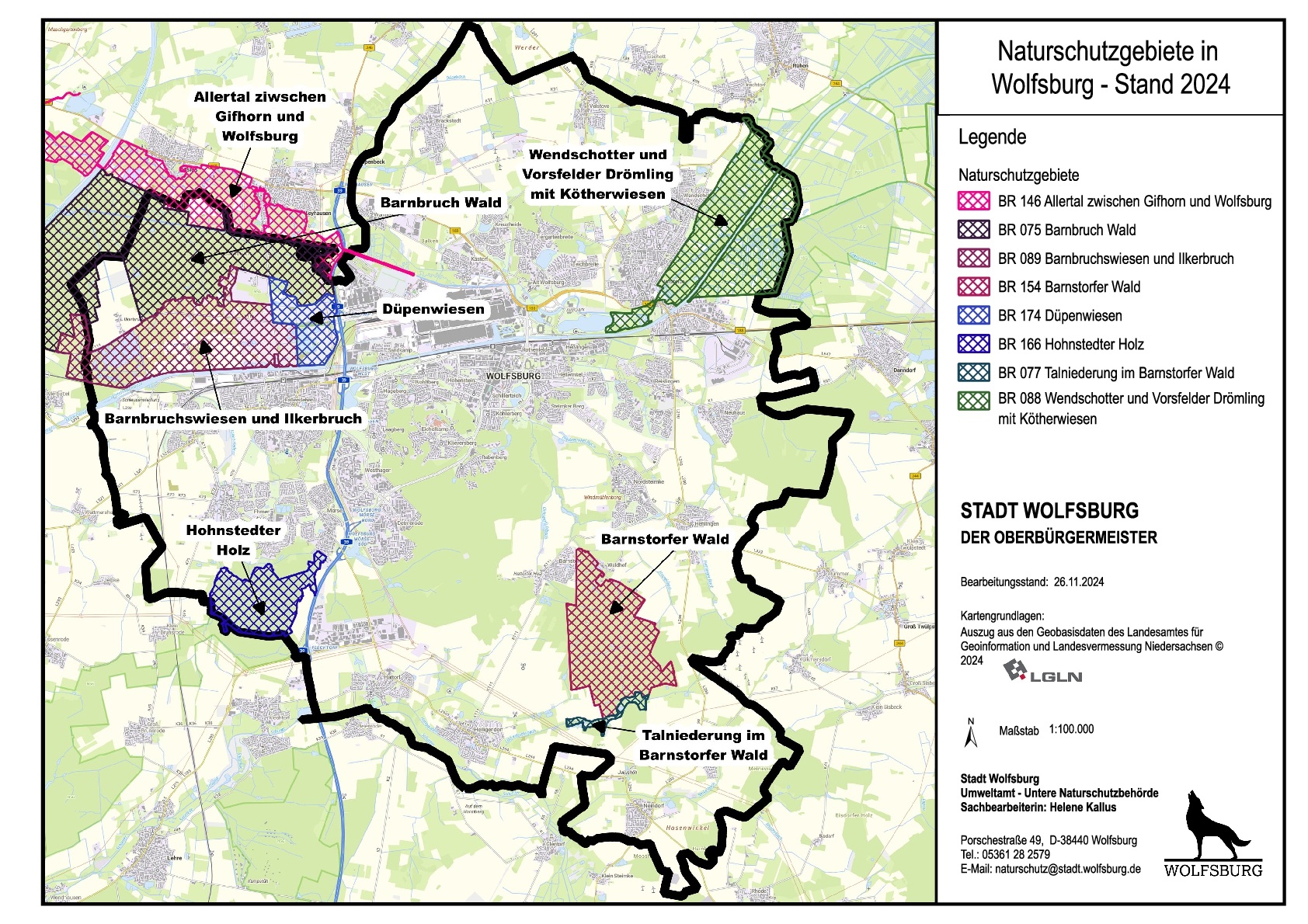 Map of the nature conservation areas in WolfsburgGraphic: Lower Nature Conservation Authority Wolfsburg
Map of the nature conservation areas in WolfsburgGraphic: Lower Nature Conservation Authority Wolfsburg -
Protected landscape areas
Landscape conservation areas are bindingly designated areas in accordance with Section 26 of the Federal Nature Conservation Act (BNatSchG) in which special protection of nature and landscape is required
- to preserve, develop or restore the performance and functionality of the ecosystem or the regenerative capacity and sustainable use of natural resources, including the protection of habitats and habitats of certain wild animal and plant species,
- because of the diversity, character and beauty or the special cultural and historical significance of the landscape or
- because of its particular importance for recreation.
In a landscape protection area, all actions that change the character of the area or run counter to the special purpose of protection are prohibited. For example, the landscape is protected from damage caused by construction or infrastructure measures.
There are the following nine landscape conservation areas in the city of Wolfsburg:
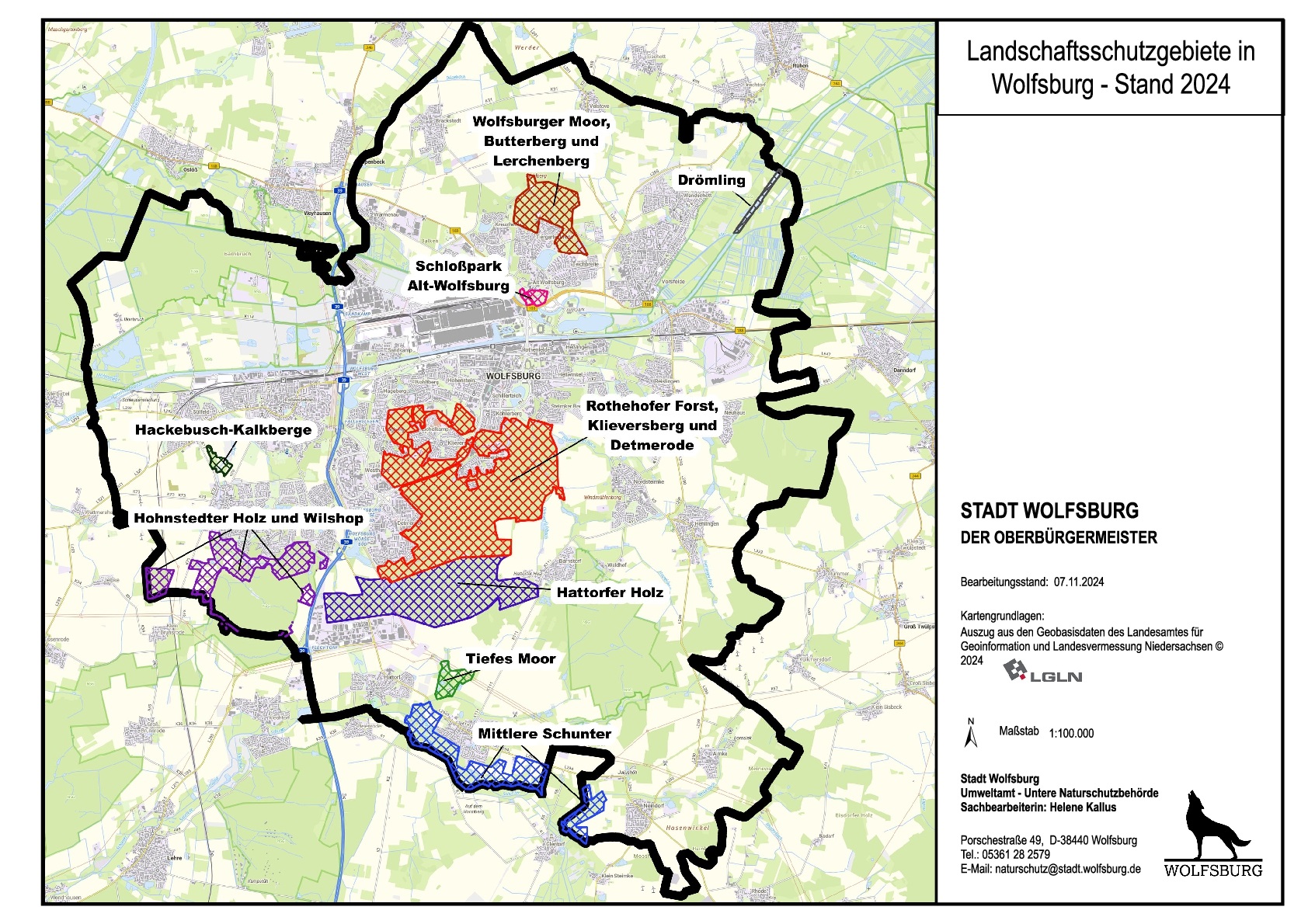 Map of the protected landscape areas in WolfsburgGraphic: Lower Nature Conservation Authority Wolfsburg
Map of the protected landscape areas in WolfsburgGraphic: Lower Nature Conservation Authority Wolfsburg- LSG WOB 001 "Rothehofer Forst, Klieversberg and Detmerode"
- LSG WOB 006 "Tiefes Moor"
- LSG WOB 007 "Hackebusch-Kalkberge"
- LSG WOB 008 "Hattorfer Holz"
- LSG WOB 009 "Hohnstedter Holz and Wilshop"
- LSG WOB 012 "Middle Schunter"
-
Drömling Biosphere Reserve
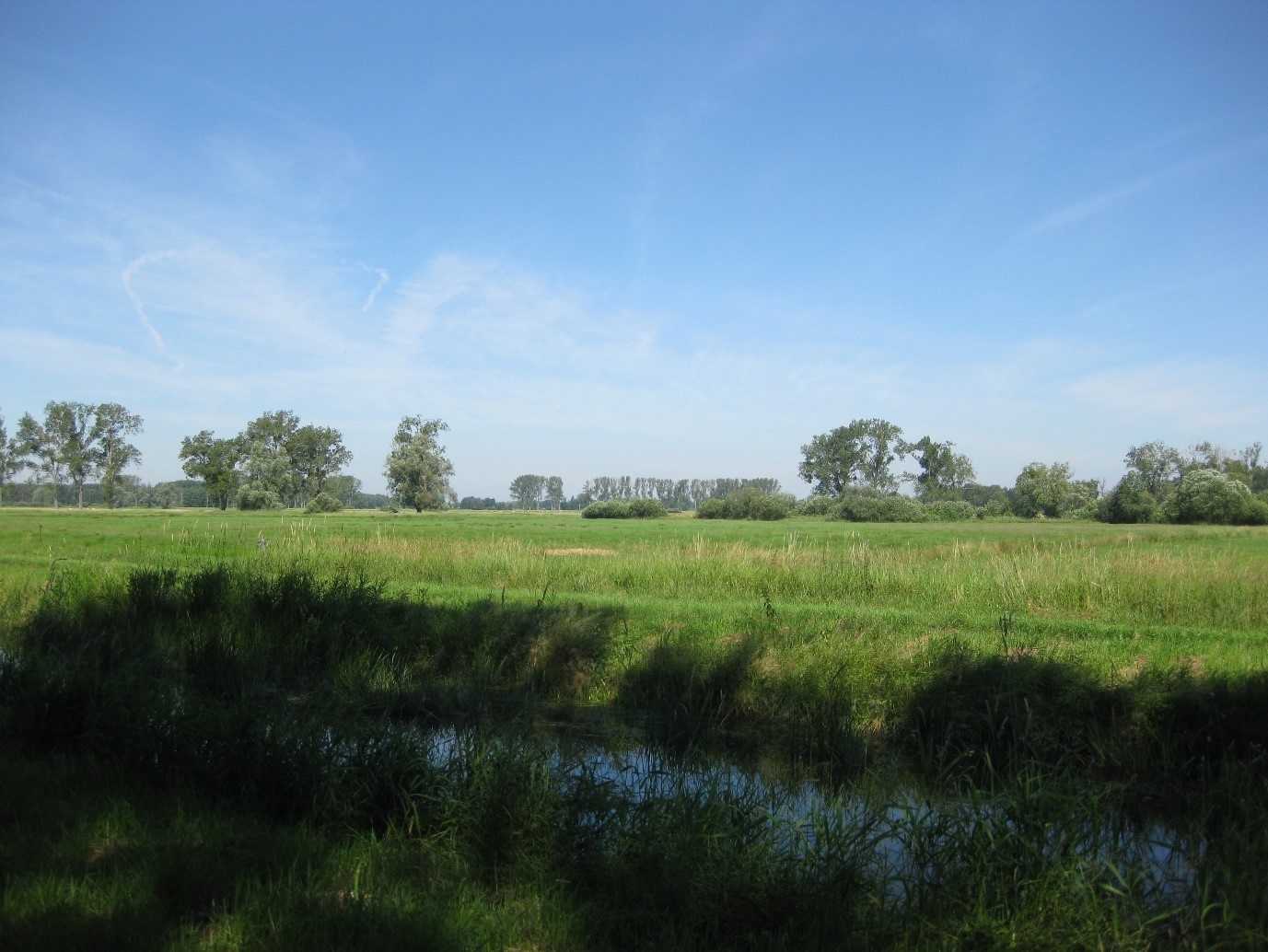 The Drömling is characterized by extensive areas of grassland, coppiced woodland and a dense system of ditches, many of which are overgrown with shrubs and trees. This unique fen landscape is home to numerous endangered plant and animal speciesPhoto: Lower Nature Conservation Authority Wolfsburg
The Drömling is characterized by extensive areas of grassland, coppiced woodland and a dense system of ditches, many of which are overgrown with shrubs and trees. This unique fen landscape is home to numerous endangered plant and animal speciesPhoto: Lower Nature Conservation Authority WolfsburgIn June 2023, the International Council of the UNESCO "Man and the Biosphere" program designated the Drömling as the 17th UNESCO biosphere reserve in Germany. The near-natural cultural landscape stretches along the former inner-German border between Saxony-Anhalt and Lower Saxony. The region, which is criss-crossed by countless watercourses, is also known as the "land of a thousand ditches".
The term "biosphere reserve" is a combination of "biosphere" (habitat) and "reserve" (from reservare = to preserve). The aim is therefore to preserve biological diversity and functioning ecosystems as the basis for sustainable economic and social development. The focus is not only on protection, but also on the appropriate use of established cultural landscapes. Only the relatively small core zones are strictly protected. In the remaining areas, the biosphere reserves test sustainable use concepts and promote nature-friendly forms of farming.
Biosphere reserves are divided into three zones of varying intensity of use:
- In the core zone, human influence is reduced to a minimum. It is largely subject to regulations for the protection of natural processes. The core zone should cover at least 3 percent of the total area of a biosphere reserve.
- In the maintenance zone, human activities such as tourism or fishing are permitted as long as they are environmentally compatible. The maintenance zone should cover at least 10 percent of the total area of the biosphere reserve, the maintenance and core zones together at least 20 percent.
- Human use is not restricted in the development zone. Voluntary participation of citizens and municipalities in a trial of measures and projects to strengthen sustainable development forms the basis for action. The development zone should cover at least 50 percent of the total area.